If you want to print your Name using C Language we Have Print Function for that (Actually more Options in C Language to Print our Names but we are going to Discuss only This Print Function methods in this Tutorial).
Where Print Function take any String or Numeric value from users and Print that Value in the Output screen when we run our C Program.
So if you want to Print your name using C Language the you need to Write Print function inside your C Program and between the Print functions double Quotes you need to write your Name.
Like : printf(“My Name“);
1) First Open You C Programming Software (Turbo C++)
2) Create New File And Save that New File With myname.c name. (here myname is out file name and .c is out C program’s Extension that will help our compiler to understand our program’s programming language.)
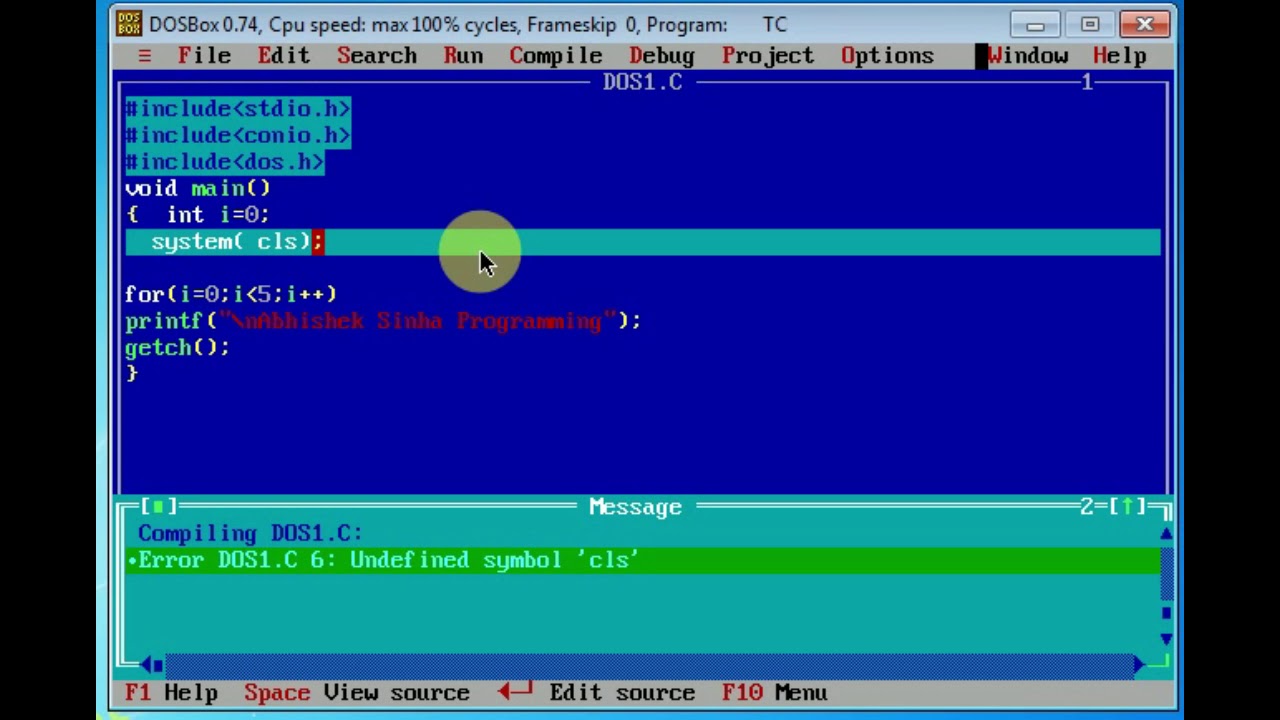
3) Write this code As shown Below:
4) Run your program by pressing ctrl+f9 (Turbo c++ user).
Print your Name using C Program
How to clear output screen using cleardevice( ) function in graphics in c using turbo c. Connect With Me! How to clear output screen using cleardevice( ) function in graphics in c using turbo. Increase your speed/productivity while you are writing program on Turbo C IDE by using Turbo C IDE shortcuts instead of mouse.
getch( ):
Usually getch() (getch function) is used to read a character from screen. But here we are using this to add a Pause to our Output Screen. If we don’t add this in our program, our program’s output screen will close quickly after running our program.
clrscr( ):
When we run our C Program for 1st time we Get our value. but after making some changes to our C program when we run the program we get out new output with the old output.
To remove those Old/Previews Output/Results values, We use clrscr();.
Where clr(Clear) and scr(Screen) stands for Clear Screen (clrscr).
Printing Name Using C Language
Results
My Name Is Human
Example (Explained):
#include<stdio.h> :
#include<stdio.h> is a Header file that includes Slandered (str) Input Output (IO) Library/File. Because All Of the C’s In build Functions are declared in <stdio.h> File
Main Function main( ) :
main() main function is the entry point of C program. When We Run our C program the execution Control Directly to the main() (main function) and gave us result in output.
Print Function printf( ) :
printf() is also a Function of C. Print function is used to print “character, string, float, integer,etc” to the output screen.
So what ever we write between printf() inverted commas (” “) that will be printed on the output Screen.
FAQ: About Print Your Name Using C Program
Write a program to display your name in c
Here is a C Program that can display your given name when you run this C Program.
We have used printf() function to Print your Name.
You also can use clrscr() Clear Screen C Function before print() Function to clear old outputs.
C program to print name and address
To print your Name or Address we can use Same C Print Function (printf()) for both.
Just write your name inside The C Function
[ printf(“Name and Address“); ].
Write a program to print your name at the center of the screen
C++ Clear Console Output
To print or write a program to print your name at the center of the screen.
We have to use C Language’s gotoxy() function.
Where we need to provide X and Y digits to Perfectly align our Name at the Center of the Screen.
Click here to learn more about C Language or Visit programminghead.com for more.
I hope this Tutorial Resolved all of your Queries about C Programming – Print Your Name Using C Program.
Thanks for visiting our Website. Have a Great Time.
- C++ Basics
- C++ Object Oriented
- C++ Advanced
- C++ Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
The C++ standard libraries provide an extensive set of input/output capabilities which we will see in subsequent chapters. This chapter will discuss very basic and most common I/O operations required for C++ programming.
C++ I/O occurs in streams, which are sequences of bytes. If bytes flow from a device like a keyboard, a disk drive, or a network connection etc. to main memory, this is called input operation and if bytes flow from main memory to a device like a display screen, a printer, a disk drive, or a network connection, etc., this is called output operation.
I/O Library Header Files
There are following header files important to C++ programs −
| Sr.No | Header File & Function and Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | <iostream> This file defines the cin, cout, cerr and clog objects, which correspond to the standard input stream, the standard output stream, the un-buffered standard error stream and the buffered standard error stream, respectively. |
| 2 | <iomanip> This file declares services useful for performing formatted I/O with so-called parameterized stream manipulators, such as setw and setprecision. |
| 3 | <fstream> This file declares services for user-controlled file processing. We will discuss about it in detail in File and Stream related chapter. |
The Standard Output Stream (cout)
The predefined object cout is an instance of ostream class. The cout object is said to be 'connected to' the standard output device, which usually is the display screen. The cout is used in conjunction with the stream insertion operator, which is written as << which are two less than signs as shown in the following example.
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
How To Clear Output Screen In Turbo C++ Free
The C++ compiler also determines the data type of variable to be output and selects the appropriate stream insertion operator to display the value. The << operator is overloaded to output data items of built-in types integer, float, double, strings and pointer values.
The insertion operator << may be used more than once in a single statement as shown above and endl is used to add a new-line at the end of the line.
The Standard Input Stream (cin)
The predefined object cin is an instance of istream class. The cin object is said to be attached to the standard input device, which usually is the keyboard. The cin is used in conjunction with the stream extraction operator, which is written as >> which are two greater than signs as shown in the following example.
When the above code is compiled and executed, it will prompt you to enter a name. You enter a value and then hit enter to see the following result −
The C++ compiler also determines the data type of the entered value and selects the appropriate stream extraction operator to extract the value and store it in the given variables.
The stream extraction operator >> may be used more than once in a single statement. To request more than one datum you can use the following −
This will be equivalent to the following two statements −
The Standard Error Stream (cerr)
The predefined object cerr is an instance of ostream class. The cerr object is said to be attached to the standard error device, which is also a display screen but the object cerr is un-buffered and each stream insertion to cerr causes its output to appear immediately.
The cerr is also used in conjunction with the stream insertion operator as shown in the following example.
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
The Standard Log Stream (clog)

The predefined object clog is an instance of ostream class. The clog object is said to be attached to the standard error device, which is also a display screen but the object clog is buffered. This means that each insertion to clog could cause its output to be held in a buffer until the buffer is filled or until the buffer is flushed.
The clog is also used in conjunction with the stream insertion operator as shown in the following example.

When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
You would not be able to see any difference in cout, cerr and clog with these small examples, but while writing and executing big programs the difference becomes obvious. So it is good practice to display error messages using cerr stream and while displaying other log messages then clog should be used.
